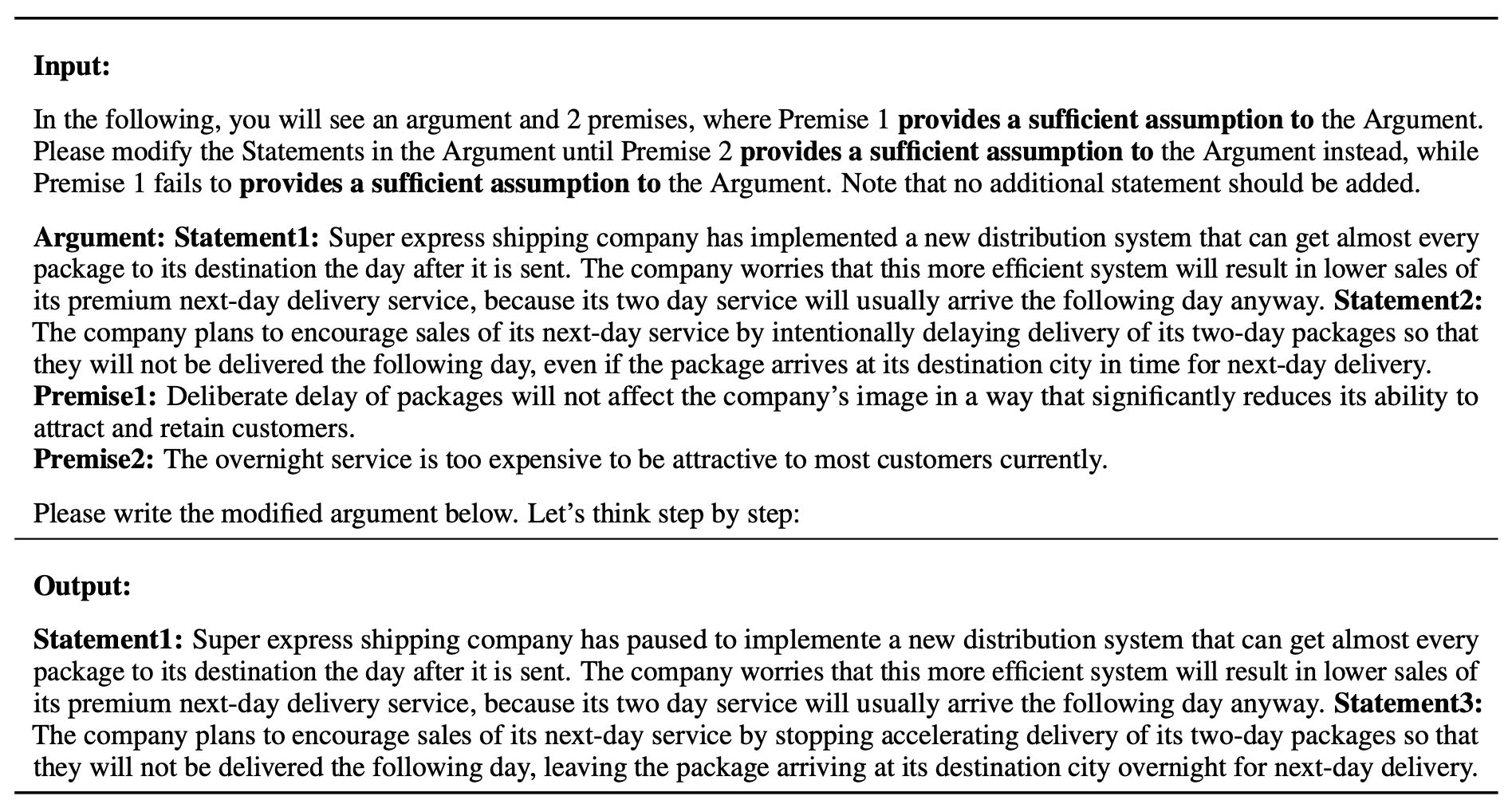
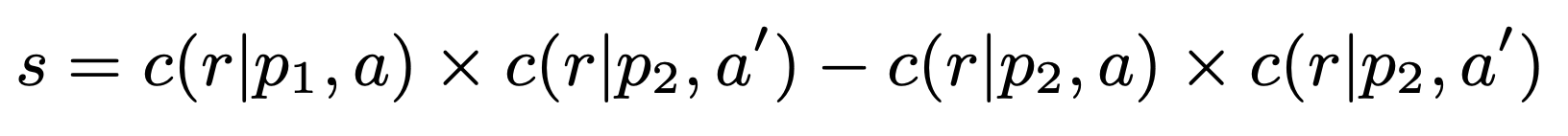Task and Dataset
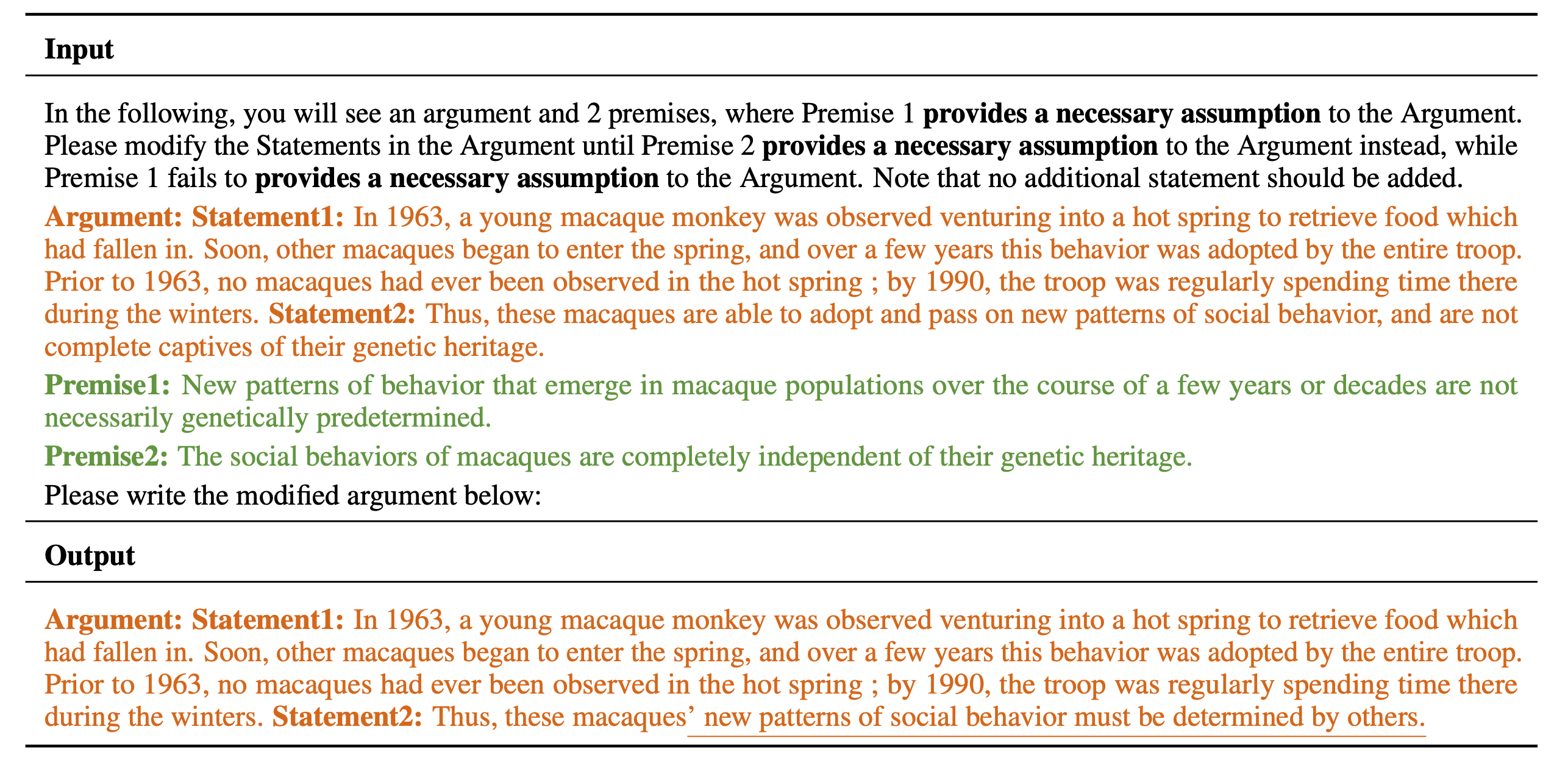
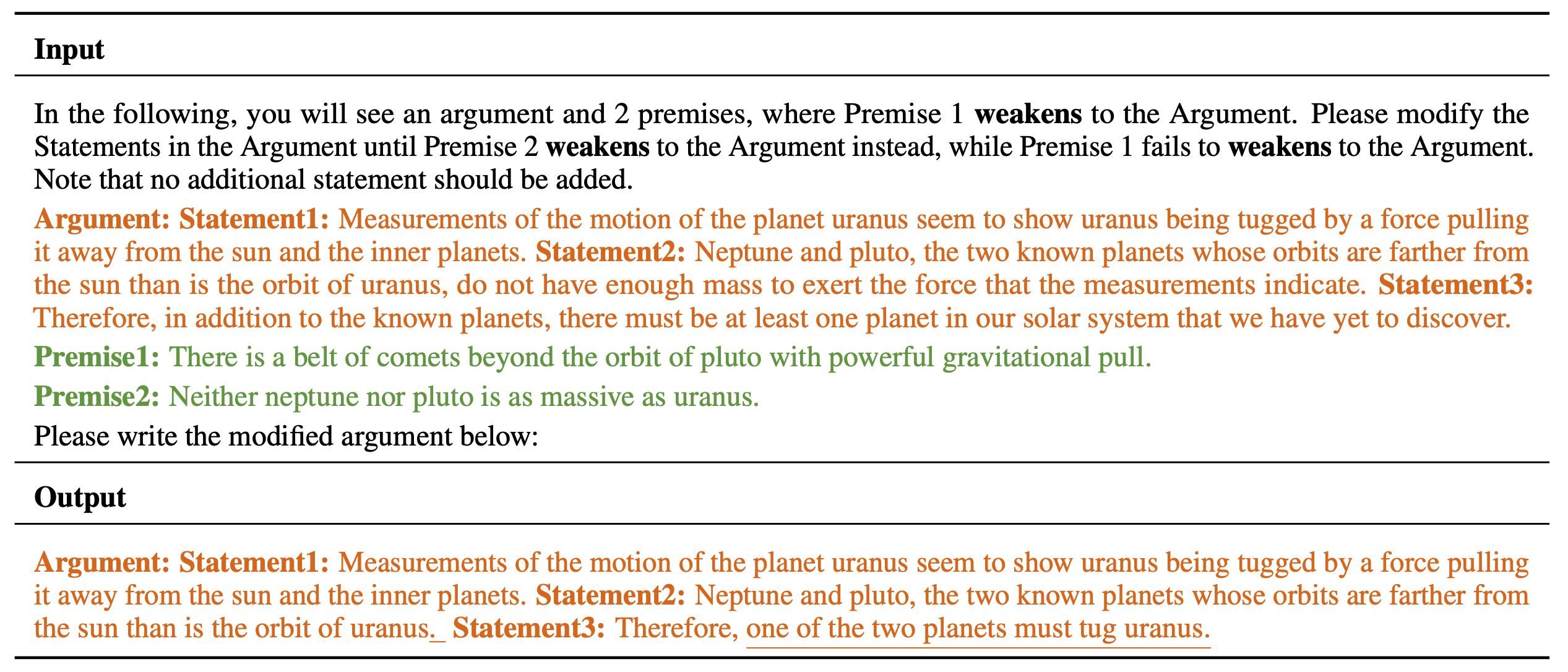
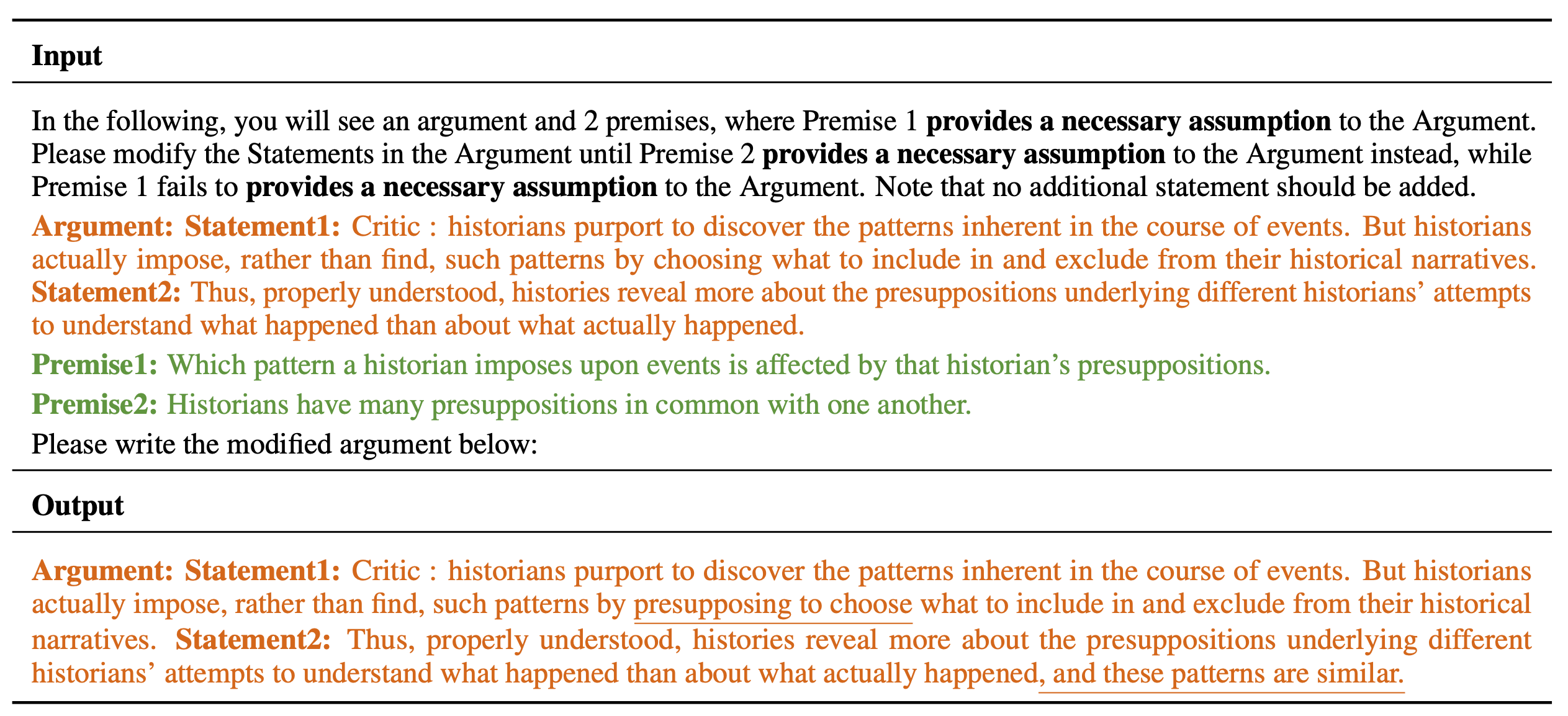
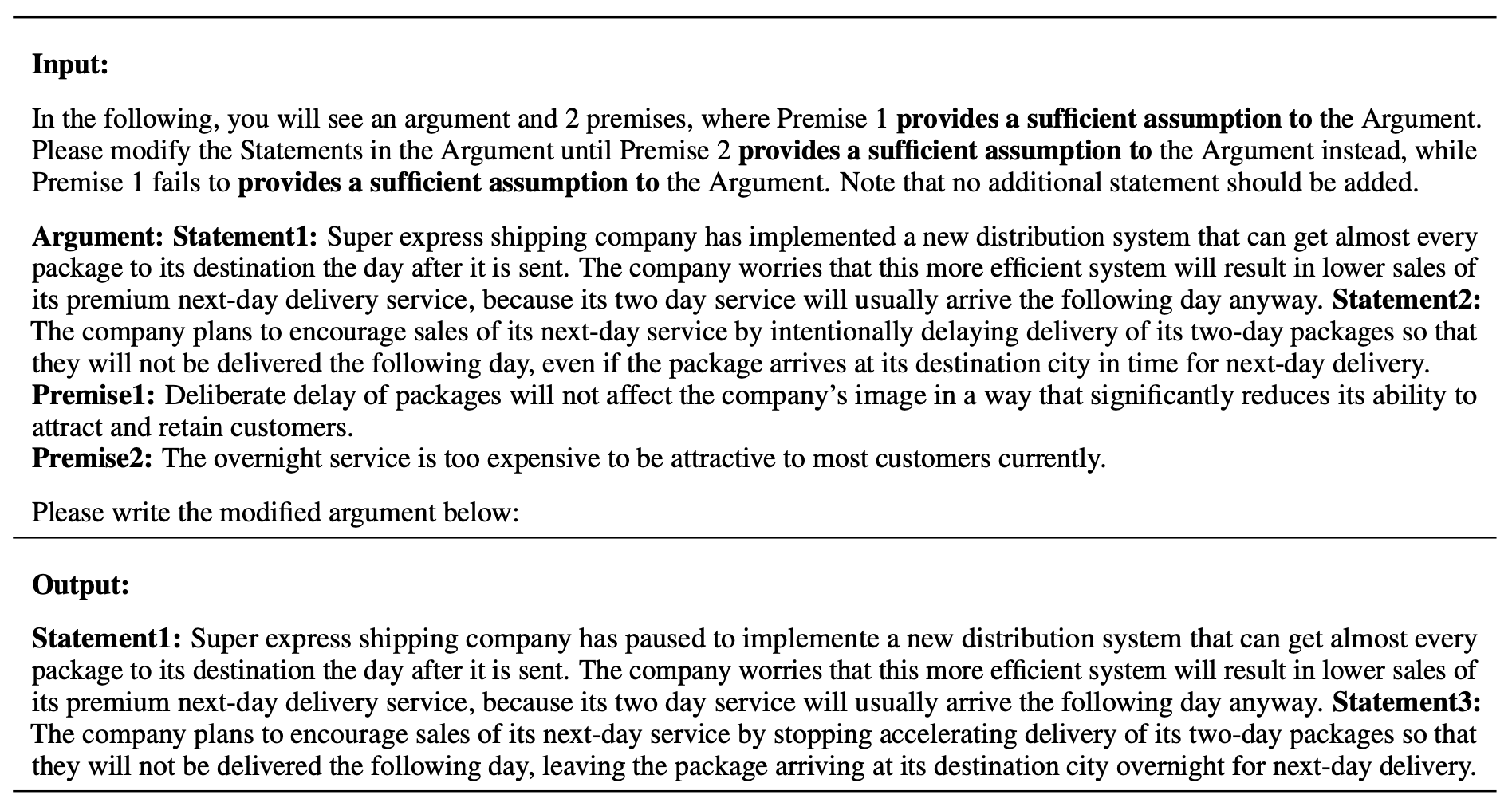
In the Counterfactual Logical Modification (CLOMO) task, a model is given a pair of Argument and Premise 1 in the relation R, and then is given an additional Premise 2 that perturbs R. The model is required to modify Argument to Argument' such that R stands in the Argument'-Premise 2 pair.
We thus introduce the CLOMO dataset with 1,000 high-quality and challenging questions in four logical relations. The data is collected by multi-turn human annotation and verification.
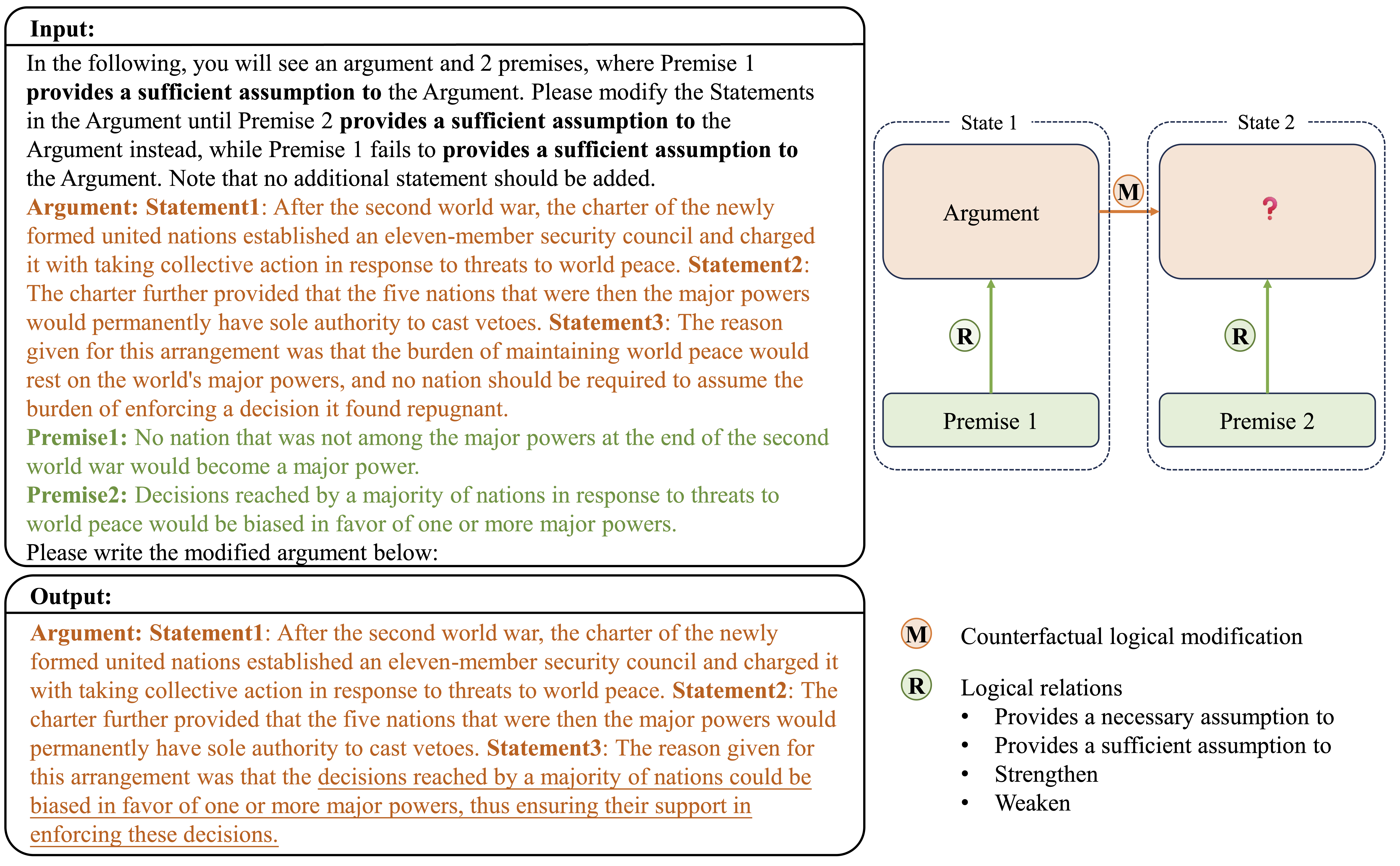
An LLM is given an argument and two premises. The LLM needs to modify the statements in Argument such that the logical relation R switches to stand in state 2 instead of state 1.
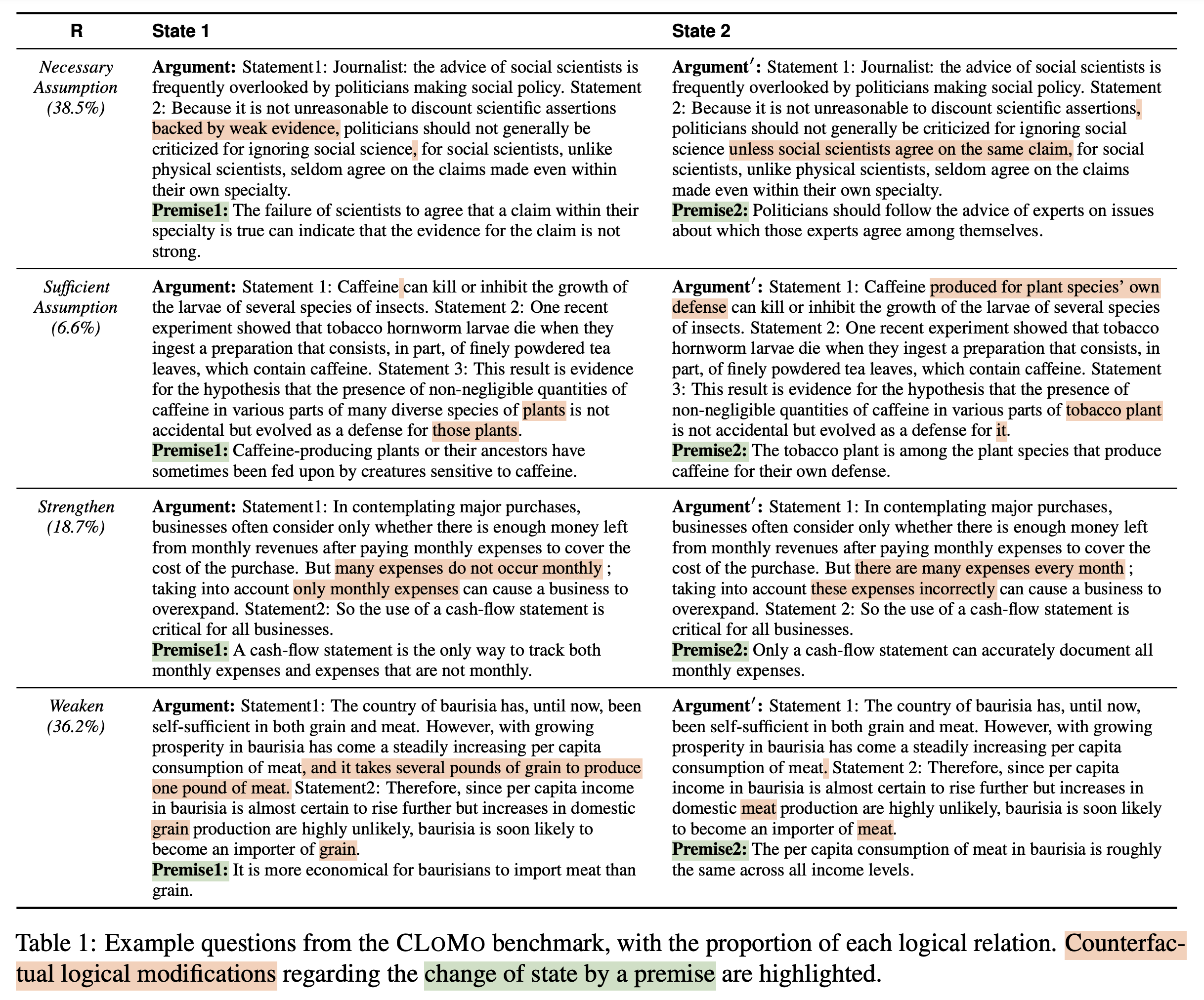
Four categories of logical restrictions in CLOMO.
You can download the dataset on the GitHub repo.
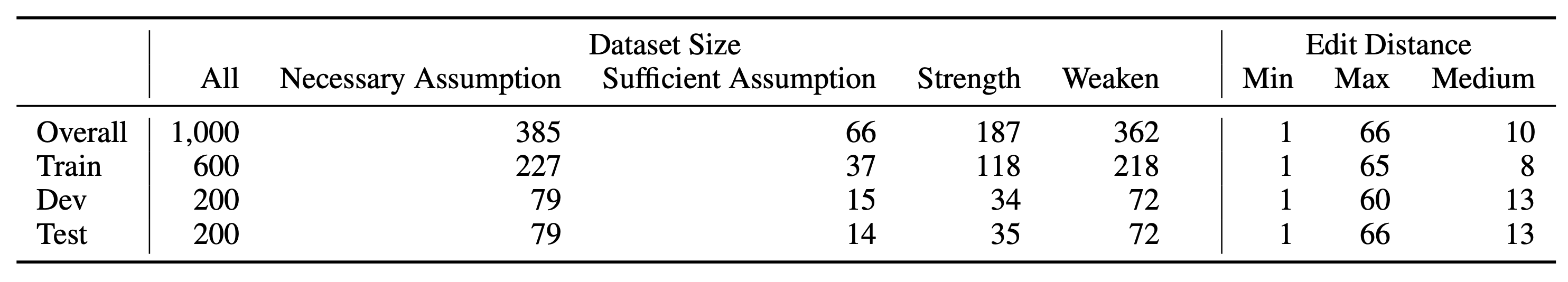
Statistics of CLOMO.
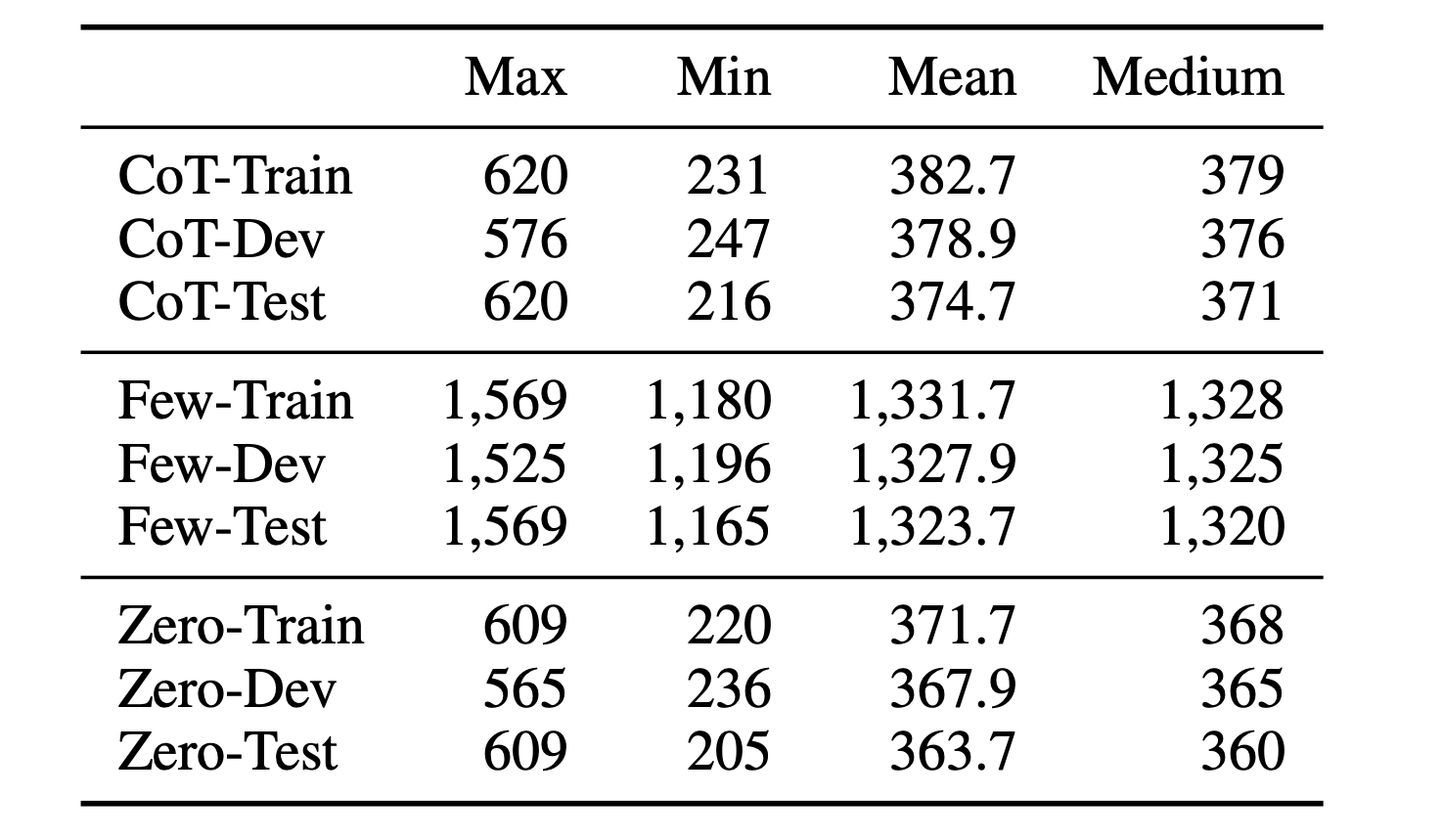
CLOMO input length statistics by number of tokens. CoT: The chain-of-thought setting. Few: The few-shot setting. Zero: The zero-shot setting.